jan . 14, 2025 10:21 Back to list
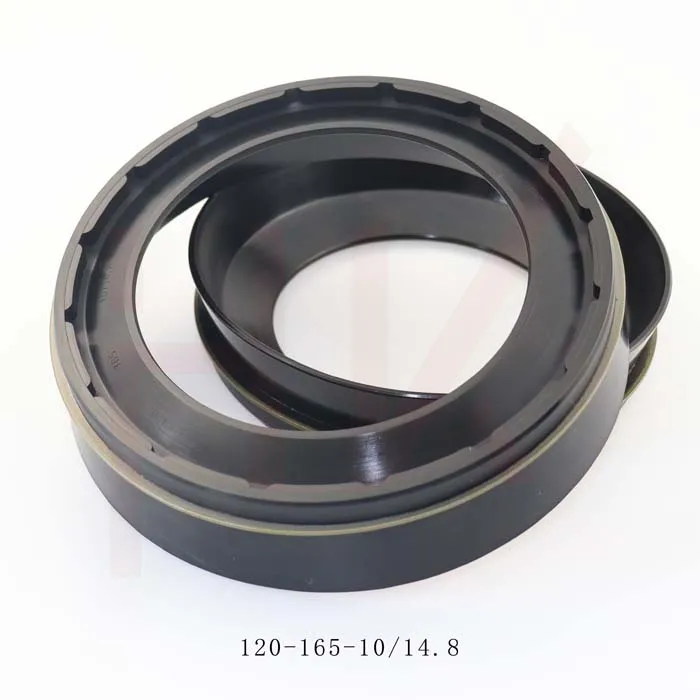
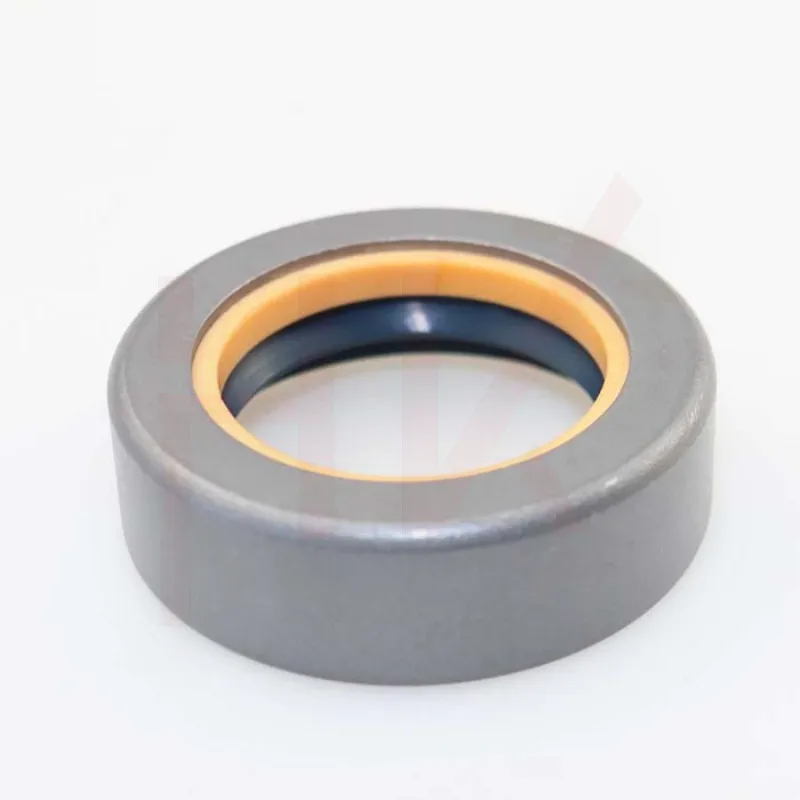
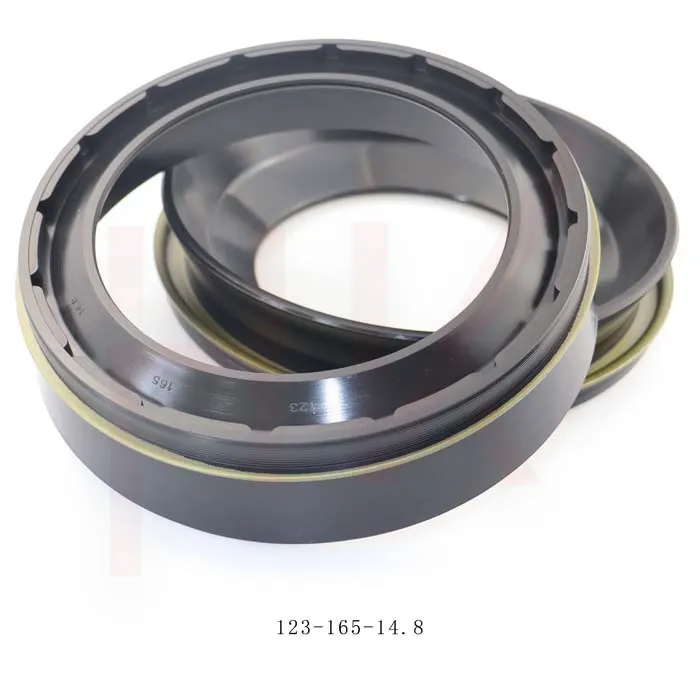
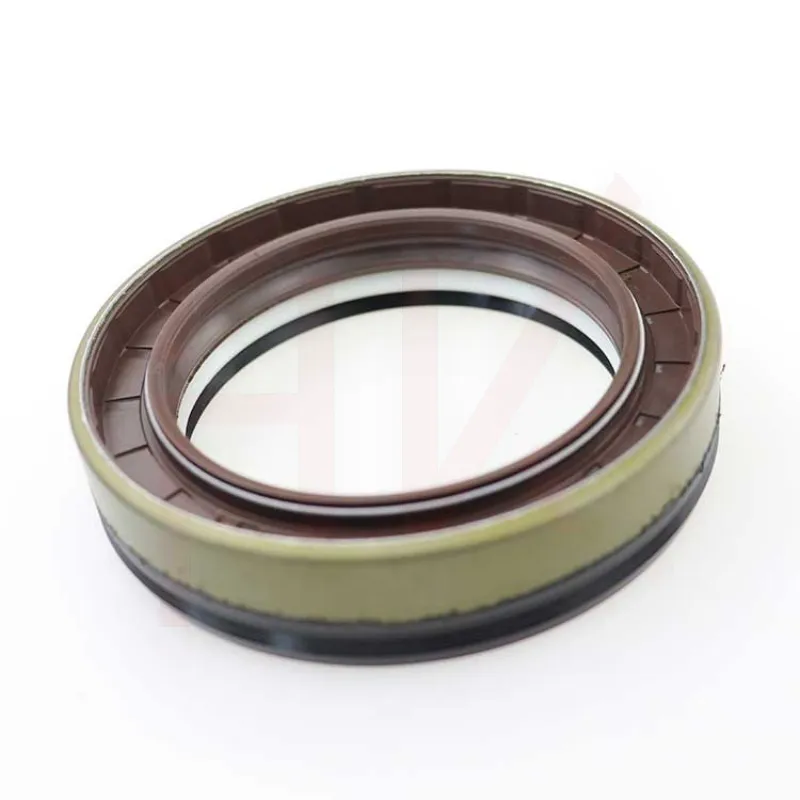
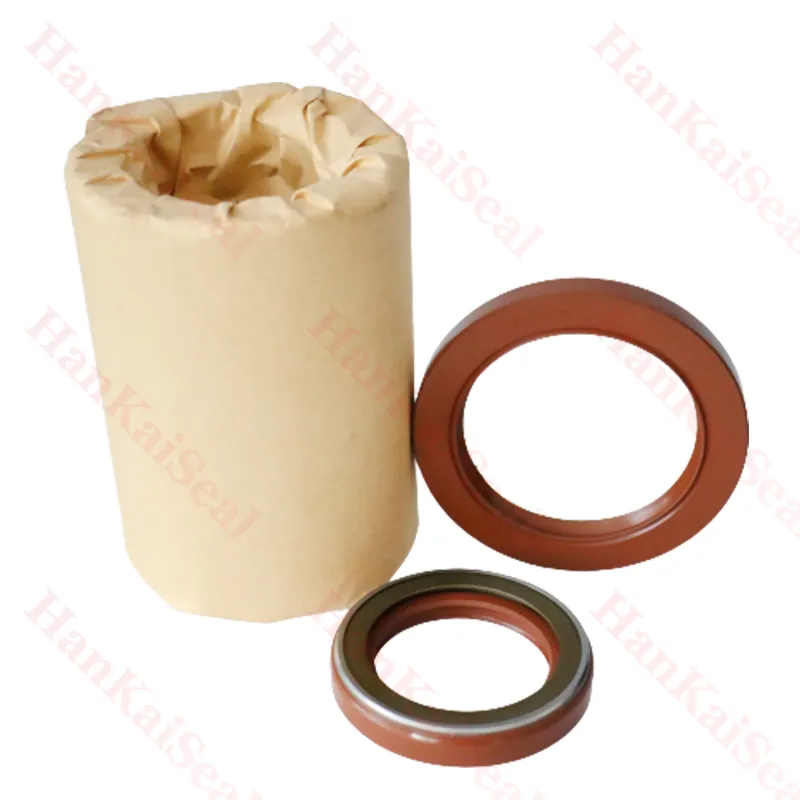
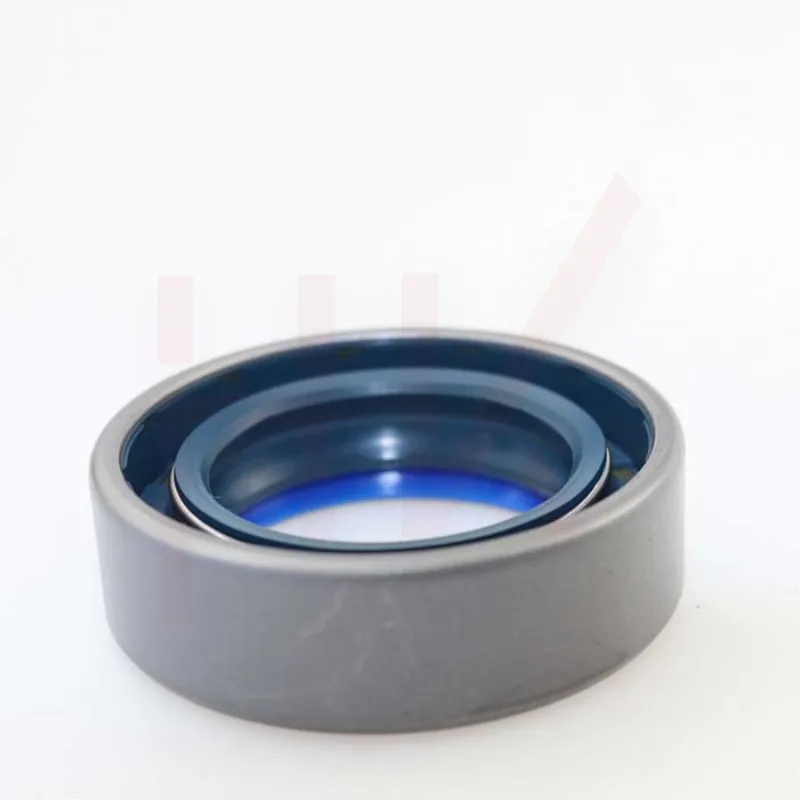
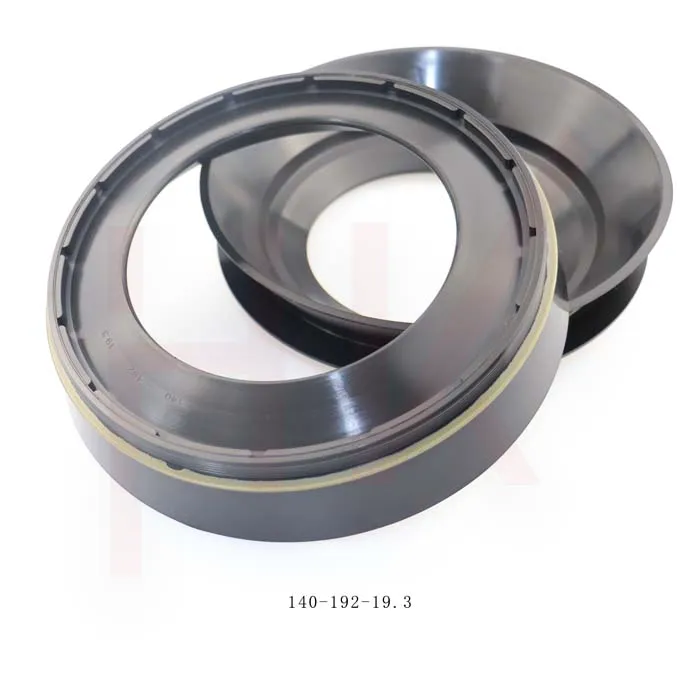
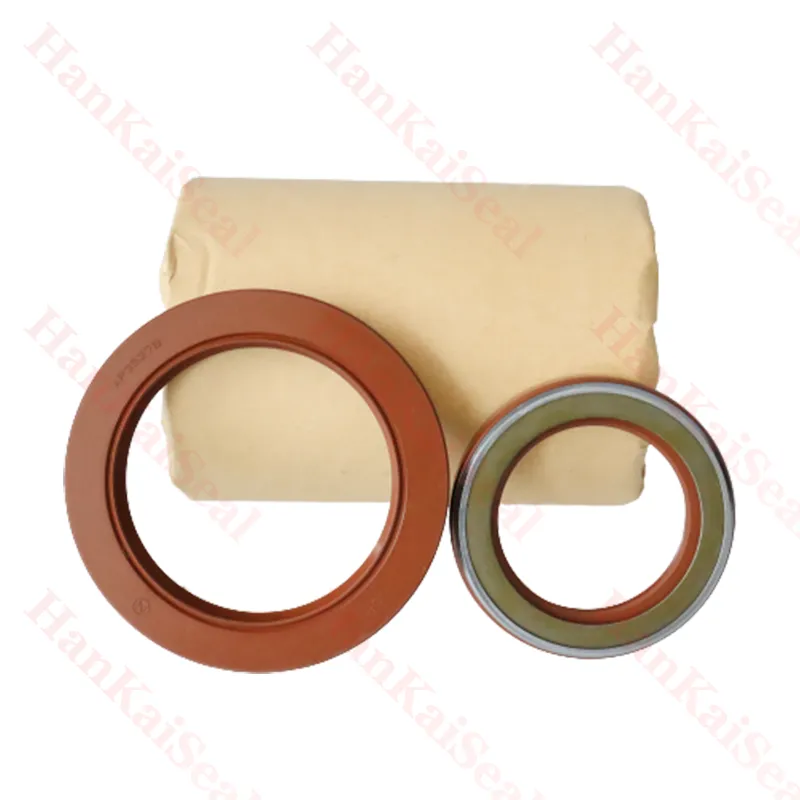
170×200×15 Rubber Oil Seal From Tcv NBR FKM High Pressure Oil Seal Tcv Oil Seal
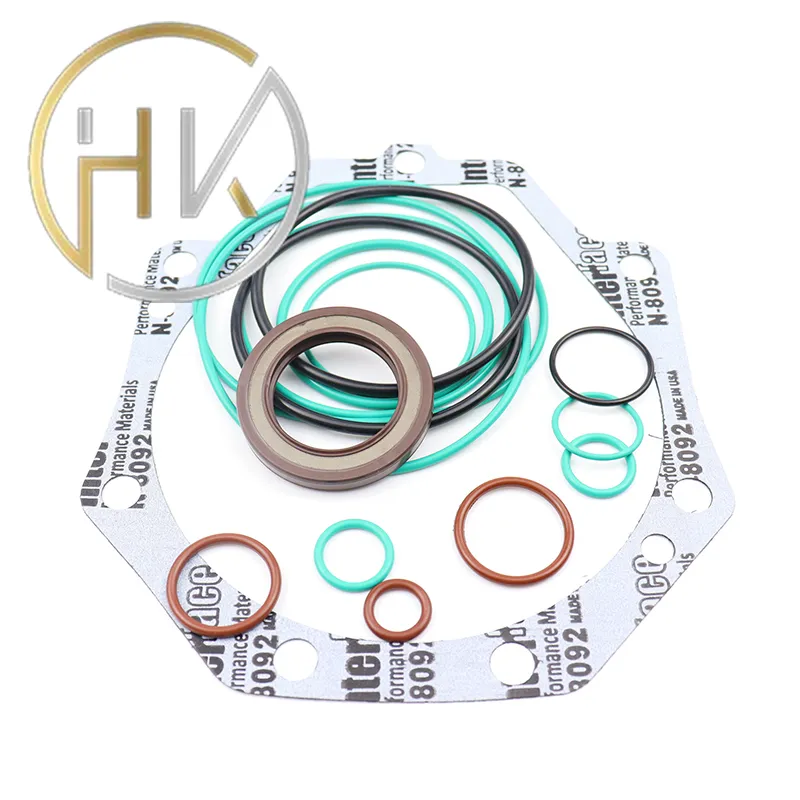

Professionals working with high-pressure seals often emphasize the importance of proper installation techniques. Misalignment during installation can lead to premature seal failure, drastically reducing service life and efficiency. Experts recommend adherence to manufacturer guidelines and the use of specialized tools and equipment to ensure precision. Furthermore, engaging experienced technicians for installation and commissioning can significantly enhance the operational lifespan of high-pressure seals. As technology evolves, so too does the manufacture and application of high-pressure seals. Innovations such as additive manufacturing and the development of nanomaterials are paving the way for next-generation seals with enhanced performance characteristics. These advancements promise even greater efficiencies and the ability to withstand harsher environments, further cementing the role of high-pressure seals in industrial applications. Selecting the right high-pressure seal is crucial and should be guided by thorough technical consultation. Factors such as compatibility with the working fluid, pressure and temperature ratings, and environmental conditions must be meticulously evaluated. Consulting with manufacturers and industry experts can facilitate the decision-making process, ensuring that the seal chosen meets the specific demands of the application. In conclusion, high-pressure seals are vital to the integrity of numerous industrial operations. Their design and selection require a deep understanding of material science and engineering principles, reinforced by real-world application knowledge. Ensuring their optimal functionality involves both innovative design and adept installation, supported by regular maintenance and technological advancements. With these considerations, high-pressure seals will continue to serve as critical enablers of industrial efficiency and safety.
-
The Trans-formative Journey of Wheel Hub Oil Seals
NewsJun.06,2025
-
Graphene-Enhanced Oil Seals: Revolutionizing High-Pressure Oil Sealing
NewsJun.06,2025
-
Future of Hydraulic Sealing: Advanced Intelligent TCN Oil Seals
NewsJun.06,2025
-
Don’t Let a Broken TCV Oil Seal Ruin Your Day
NewsJun.06,2025
-
Bio-Inspired Dust Seals for Better Sealing Performance
NewsJun.06,2025
-
Biodegradable and Sustainable Hydraulic Seal Materials
NewsJun.06,2025
-
Top Oil Seal Solutions for Your Industrial Needs
NewsMay.22,2025
Products categories
















